Isaac ROS Deep segmentation
Isaac ROS Depth Segmentation official website link:https://nvidia-isaac-ros.github.io/repositories_and_packages/isaac_ros_depth_segmentation/index.html
Overview
Isaac ROS Depth Segmentation provides NVIDIA NVIDIA-accelerated packages for depth segmentation. Theisaac_ros_bi3dpackage uses the optimized Bi3D DNN model to perform stereo-depth estimation via binary classification, which is used for depth segmentation. Depth segmentation can be used to determine whether an obstacle is within a proximity field and to avoid collisions with obstacles during navigation.
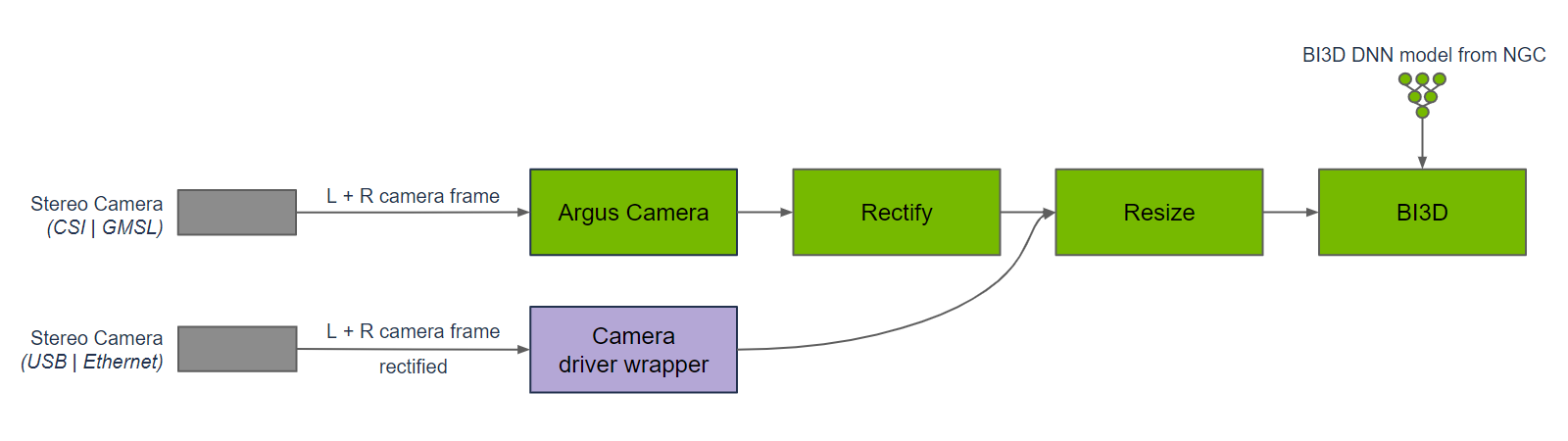
Bi3D is used in a graph of nodes to provide depth segmentation from a time-synchronized input left and right stereo image pair. Images to Bi3D need to be rectified and resized to the appropriate input resolution. The aspect ratio of the image needs to be maintained; hence, a crop and resize may be required to maintain the input aspect ratio. The graph for DNN encode, to DNN inference, to DNN decode is part of the Bi3D node. Inference is performed using TensorRT, as the Bi3D DNN model is designed to use optimizations supported by TensorRT.
Compared to other stereo disparity functions, depth segmentation provides a prediction of whether an obstacle is within a proximity field, as opposed to continuous depth, while simultaneously predicting freespace from the ground plane, which other functions typically do not provide. Also unlike other stereo disparity functions in Isaac ROS, depth segmentation runs on NVIDIA DLA (deep learning accelerator), which is separate and independent from the GPU.
Quick Experience
To simplify development, we primarily use the Isaac ROS Dev Docker image and demonstrate the effects there. This demonstration does not require any camera device installation; it simulates the camera data stream by playing a rosbag file.
Note: If you wish to install on your own device or connect a camera to develop other features, please refer to the Isaac ROS official website and connect to an NVIDIA-specified camera model for your own development.
Open a terminal and enter the working directory
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src
Enter the Isaac ROS Dev Docker container
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \
./scripts/run_dev.sh
Run the following startup command
ros2 launch isaac_ros_examples isaac_ros_examples.launch.py \
launch_fragments:=bi3d \
interface_specs_file:=${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/isaac_ros_bi3d/rosbag_quickstart_interface_specs.json \
featnet_engine_file_path:=${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/models/bi3d_proximity_segmentation/featnet.plan \
segnet_engine_file_path:=${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/models/bi3d_proximity_segmentation/segnet.plan \
max_disparity_values:=10
Open a second terminal and enter the container
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \
./scripts/run_dev.sh
Run the following command
ros2 bag play --loop ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/isaac_ros_assets/isaac_ros_bi3d/bi3dnode_rosbag
View the results
Open a third terminal and enter the container
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \
./scripts/run_dev.sh
Run the following command to view the depth segmentation map
ros2 run isaac_ros_bi3d isaac_ros_bi3d_visualizer.py --max_disparity_value 30
Open the fourth terminal and enter the container
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \
./scripts/run_dev.sh
Run the following command to view the image
ros2 run image_view image_view --ros-args -r image:=right/image_rect
